0086-18057388688
The Versatile World of Knitted Fabric: Properties, Uses, and Advantages
Release Date : 2025.06.06
Knitted fabric is one of the most essential and widely used textiles in the modern world, offering a unique blend of comfort, flexibility, and functionality. From fashion to industrial applications, knitted fabric plays a pivotal role in our daily lives.
What is Knitted Fabric?
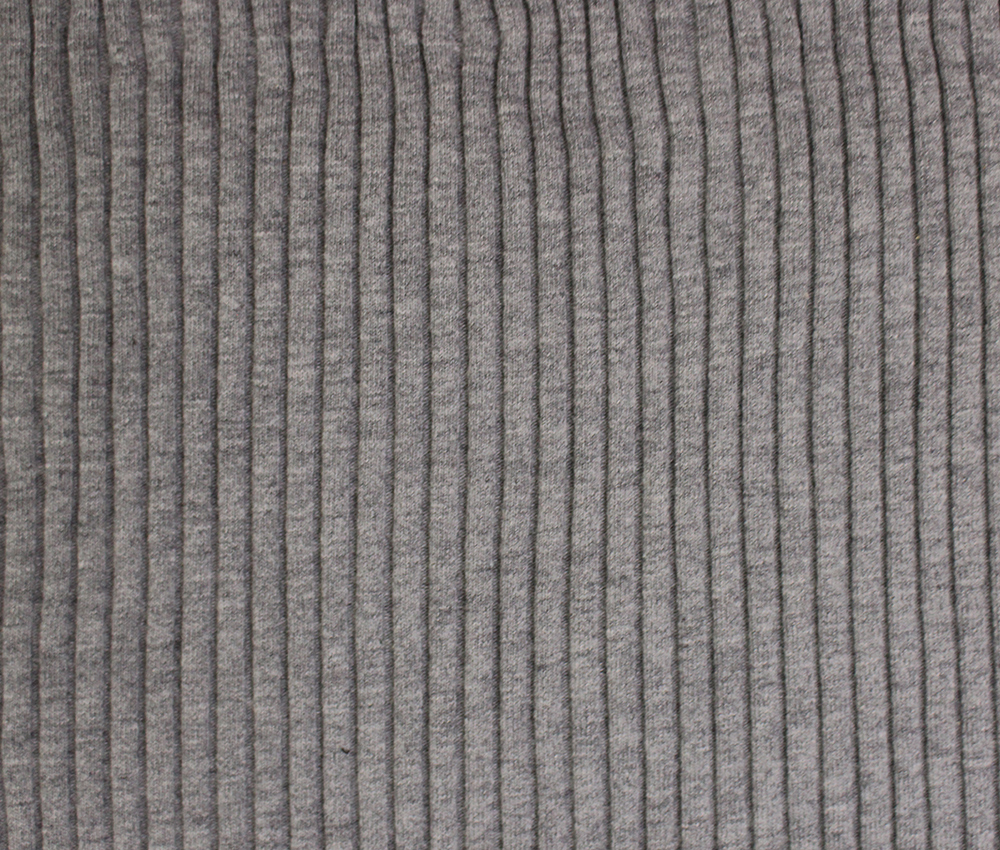
- Definition: Knitted fabric is a textile that is made by interlooping yarns, creating a series of connected loops. Unlike woven fabrics, which are produced by interlacing yarns at right angles, knitted fabric is formed using needles that pull loops of yarn through one another.
- Structure: The looped structure provides knitted fabric with natural elasticity, breathability, and softness.
- Materials Used: Common materials used to create knitted fabric include cotton, polyester, wool, silk, and blends of natural and synthetic fibers.
Types of Knitted Fabric
- Weft Knitted Fabric: Created using a single yarn looped horizontally, examples include jersey knit and rib knit. This type is highly stretchable and commonly used in t-shirts and casual wear.
- Warp Knitted Fabric: Made using multiple yarns looped vertically, it is more stable and less stretchy. Tricot and raschel are popular warp knits used in lingerie and sportswear.
- Circular and Flat Knits: Circular knitting machines create tubular fabrics, while flat knitting machines produce flat panels. Each method serves different garment construction needs.
Key Characteristics of Knitted Fabric
- Elasticity: Knitted fabric has excellent stretchability, making it ideal for form-fitting garments and activewear.
- Breathability: The loops allow air to circulate, offering better ventilation compared to woven fabrics.
- Softness and Comfort: The structure and materials used in knitted fabric contribute to a soft texture, suitable for next-to-skin garments.
- Wrinkle Resistance: Knitted fabric resists creasing, making it a low-maintenance textile.
- Durability: Despite its softness, high-quality knitted fabric can be highly durable and resistant to wear and tear.
Applications of Knitted Fabric
Fashion and Apparel:
- T-shirts, hoodies, dresses, and leggings
- Undergarments and lingerie due to flexibility and comfort
Sportswear and Activewear:
- Jerseys, compression garments, and performance wear benefit from the fabric’s stretch and moisture-wicking properties
Home Textiles:
- Blankets, cushion covers, and fitted sheets
Medical and Industrial Uses:
- Compression stockings, bandages, and technical textiles for automotive or aerospace industries
Advantages of Knitted Fabric Over Woven Fabric
- Greater Comfort: Due to its elasticity and softness, knitted fabric is more comfortable for prolonged wear.
- Easy Care: It requires less ironing and is often machine washable, saving time and effort.
- Enhanced Movement: Ideal for active lifestyles, knitted fabric moves with the body rather than restricting it.
- Creative Design Possibilities: The versatility of knitting patterns and materials allows for innovative designs in both fashion and technical textiles.
Caring for Knitted Fabric
Washing Tips:
- Use gentle cycles and mild detergents to preserve elasticity and shape.
Drying Methods:
- Air-dry when possible to prevent shrinking or damage from heat.
Storage Recommendations:
- Fold rather than hang to avoid stretching or distorting the fabric.
Sustainability and the Future of Knitted Fabric
Eco-Friendly Options:
- Organic cotton and recycled polyester are becoming popular choices for sustainable knitted fabric.
Technological Advancements:
- Smart textiles and 3D knitting technologies are pushing the boundaries of what knitted fabric can do.
Circular Fashion:
- Knitted fabric is increasingly featured in clothing lines designed for recycling and repurposing, contributing to a more sustainable fashion industry.